Definition: Bollinger Bands are a type of price envelope developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s. They consist of three lines: a middle band (usually a simple moving average), an upper band, and a lower band. The upper and lower bands are standard deviations away from the middle band, creating a dynamic range that expands and contracts with volatility.
Purpose: Bollinger Bands help traders identify overbought and oversold conditions, volatility, and potential reversal points. They are particularly useful for spotting price breakouts and trend continuations.
Example:
Components:
Calculation:
Example:
Purpose: Bollinger Bands help traders identify when an asset is overbought or oversold by observing its position relative to the bands.
Example:
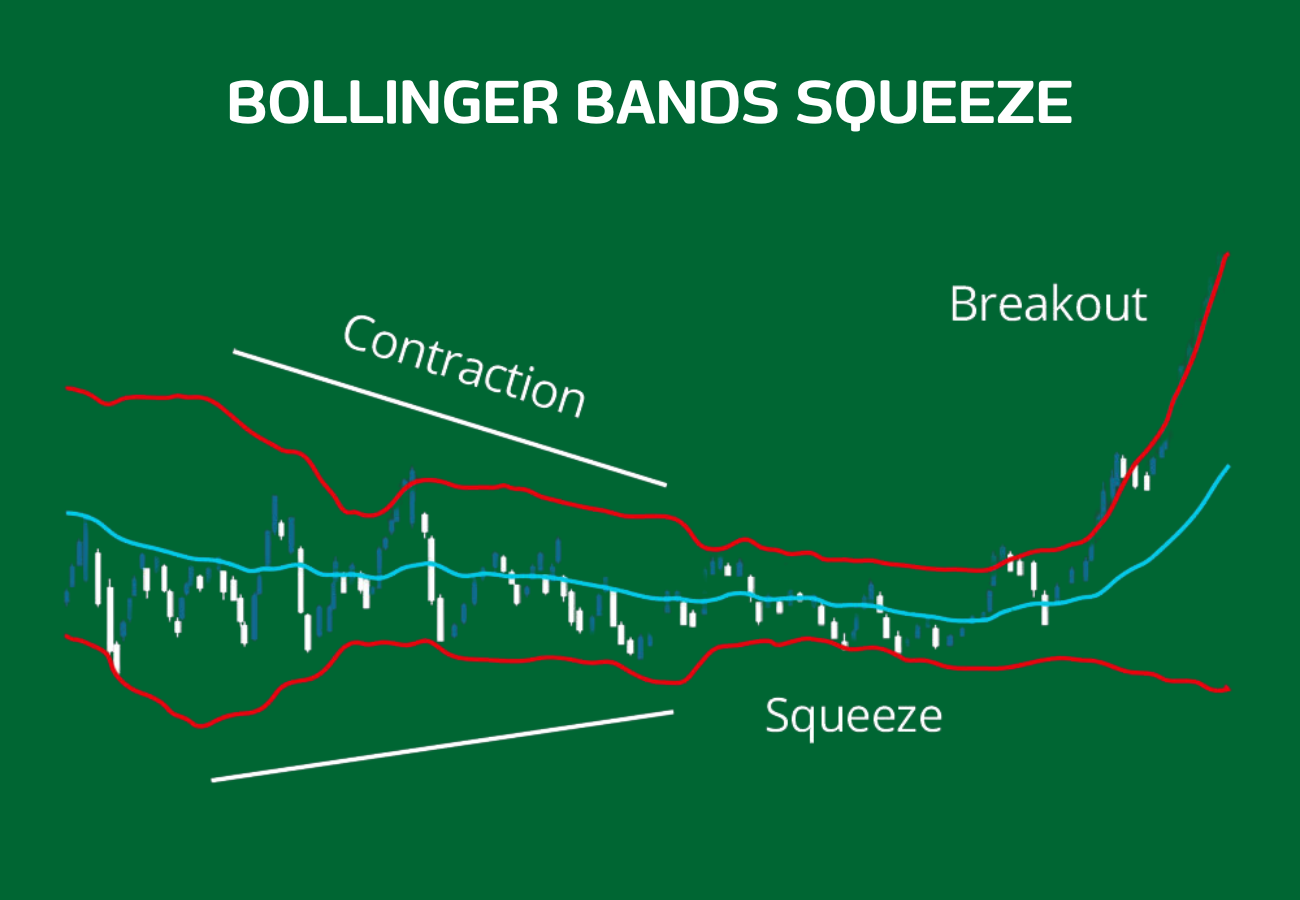
Definition: The Bollinger Band Squeeze occurs when the bands come close together, indicating low volatility. This often precedes a significant price move.
Example:
Definition: A breakout occurs when the price moves above the upper band or below the lower band. This can signal the start of a new trend.
Example:
Definition: Bollinger Bands adjust to market conditions, expanding during high volatility and contracting during low volatility.
Example:
Definition: Bollinger Bands can be used with other indicators and across different timeframes, making them a versatile tool for traders.
Example:
Definition: Bollinger Bands can sometimes generate false signals, especially in trending markets where prices can remain overbought or oversold for extended periods.
Example:
Definition: The use of standard deviation assumes that price movements are normally distributed, which is not always the case in financial markets.
Example:
Bollinger Bands are a powerful tool in technical analysis, providing insights into volatility, overbought and oversold conditions, and potential breakouts. By understanding how to interpret and apply Bollinger Bands effectively, you can enhance your trading strategy and make more informed decisions in the Forex market.
Stay tuned for more intermediate-level educational content as we continue to explore advanced trading concepts with AcademicFX. Happy trading!
Dive deeper into technical analysis with our intermediate-level video on using Divergence and Bollinger Bands. This comprehensive guide will teach you how to identify potential market reversals and profitable trading opportunities, enhancing your trading skills and strategy execution.
Tags :
AcademicFX, Bollinger Bands, INDICATORS
Copyright © 2024 ACADEMICEDU LIMITED
Unlock full access to our comprehensive educational content and advanced trading strategies by upgrading to our premium levels. Invest in your trading education and become a confident, successful trader with AcademicFX.
