Supply and demand zones are specific areas on a price chart where there is a significant imbalance between buyers and sellers. These zones indicate where the market has previously reacted strongly, either through a rally (demand) or a decline (supply). The types of supply and demand can be broadly categorized based on their formation and market context.
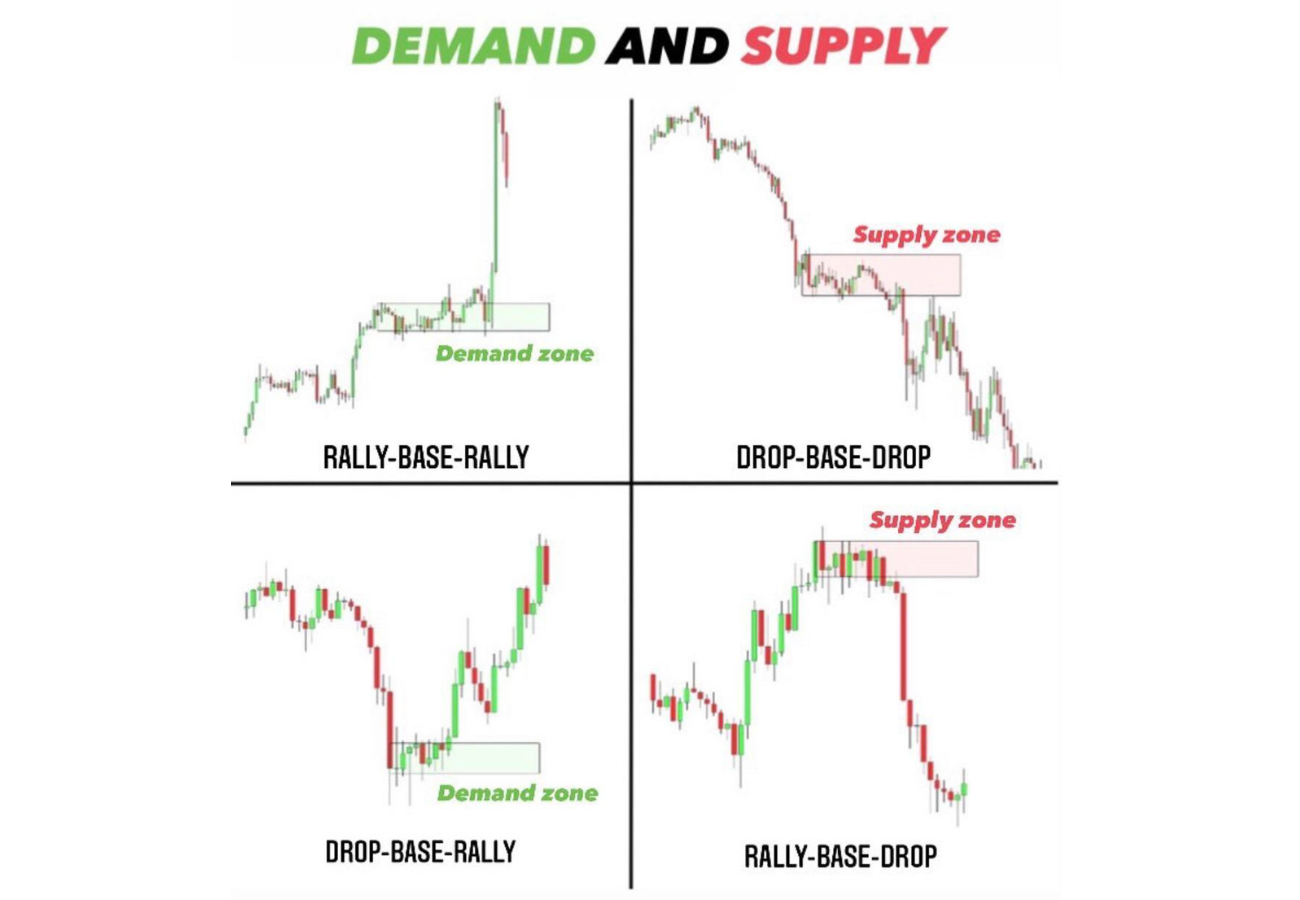
Rally-Base-Rally (RBR) Demand Zone:
Drop-Base-Rally (DBR) Demand Zone:
Drop-Base-Drop (DBD) Supply Zone:
Rally-Base-Drop (RBD) Supply Zone:
Volume:
Time Spent in the Zone:
Price Movement Before and After the Zone:
Market Context:
Identifying Trade Opportunities:
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels:
Combining with Other Technical Analysis Tools:
Understanding the different types of supply and demand zones is essential for traders looking to implement the Supply and Demand trading strategy effectively. By identifying Rally-Base-Rally (RBR) and Drop-Base-Rally (DBR) demand zones, as well as Drop-Base-Drop (DBD) and Rally-Base-Drop (RBD) supply zones, traders can anticipate potential price movements and make informed trading decisions. Incorporating factors such as volume, time spent in the zone, price movement, and broader market context further refines the analysis and enhances the strategy’s effectiveness. With careful application and disciplined execution, the Supply and Demand trading strategy can be a valuable tool for achieving consistent trading success.
Stay tuned for more educational content as we delve deeper into advanced trading concepts with AcademicFX.
Happy trading!
Tags :
AcademicFX, Types of Supply and Demand
Copyright © 2024 ACADEMICEDU LIMITED
Unlock full access to our comprehensive educational content and advanced trading strategies by upgrading to our premium levels. Invest in your trading education and become a confident, successful trader with AcademicFX.
